Dow Filmtec LE-4040 Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membrane
2,500 GPD industrial / commercial low energy replacement reverse osmosis (RO) membrane element
Filmtec brackish water reverse osmosis membrane elements provide consistent, outstanding system performance in light industrial applications. Filmtec LE-4040 delivers highest performance at lowest pressure resulting in less energy usage and lower costs. Elements with a hard shell exterior are recommended for systems with multiple-element housings containing three or more membranes, as they are designed to withstand higher pressure drops.
LE-4040 replaces BW30LE-4040.
|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
*Permeate flow and salt rejection based on the following test conditions: 2,000 ppm NaCl, applied pressure of 150 psig (10.3 bar) , 77F (25C) and 15% recovery. Permeate flows for individual elements may vary +/-20%.
**Under certain conditions, the presence of free chlorine and other oxidizing agents will cause premature membrane failure. Since oxidation damage is not covered under warranty, Dow recommends removing residual free chlorine by pretreatment prior to membrane exposure. Most RO systems have carbon pre-filters for this purpose.
***Maximum temperature for continuous operation above pH 10 is 95F (35C).
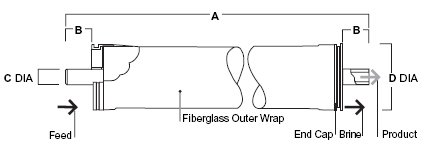
Dimensions:
|
A: 40.0" (1,016mm) B: 1.05" (26.7mm) C: 0.75" (19mm) D: 3.9" (99mm) |
 |
| Model | Diameter Inches | Length Inches | Active Surface Area ft2 (m2) |
Test Pressure | Permeate Flow Capacity GPD (m3/day) |
Price (w/ Free Shipping) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filmtec LE-4040 Our Stock #703275173 Dow Part #275173 |
4.0 | 40 | 78 (7.2) | 150 psi | 2,500 (9.5) | Sorry, this membrane has been discontinued. Recommended Replacement: Filmtec LC LE-4040 |
Notice: The use of this product in and of itself does not necessarily guarantee the removal of cysts and pathogens from water. Effective cyst and pathogen reduction is dependent on the complete system design and on the operation and maintenance of the system.




